Weight management
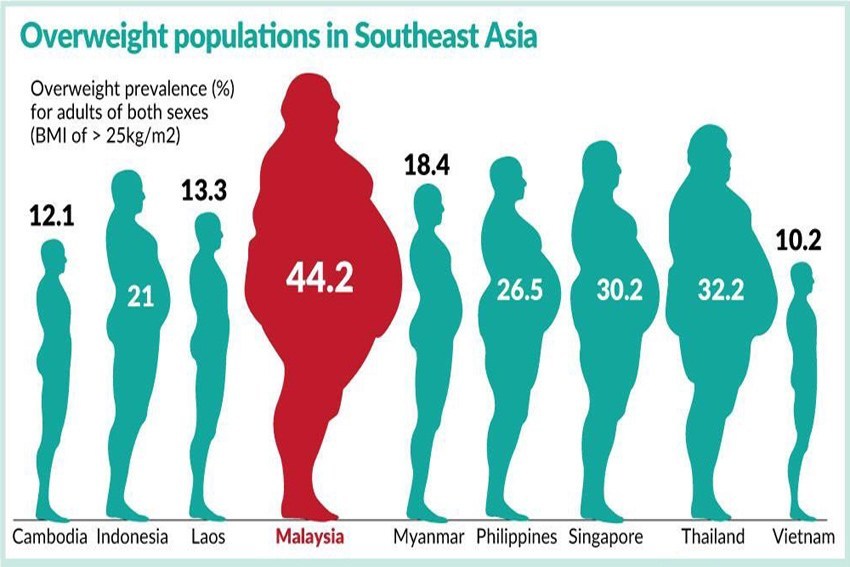
Malaysia has a high rate of obesity. In fact, we have the highest rate of obesity among all the Asian countries. This diagram illustrates the proportion of adults that are overweight in Asean countries, and clearly, we are a bigger population compared to our peers.

What counts as overweight/obesity?
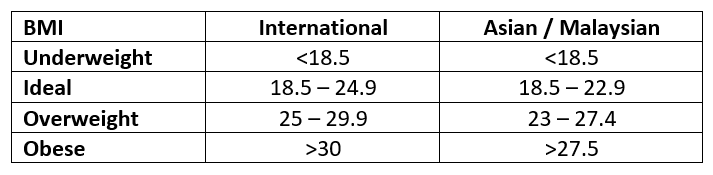
The body mass index (BMI) is used to classify overweight and obesity in adults. To calculate BMI, the following formula is used:
BMI = weight (kg) / height2 (m)
The international and Asian (including Malaysian) cutoff for BMI is slightly different. For Malaysians, the ideal BMI is between 18.5-22.9 kg/m2.
What are the complications of obesity?
The list is very long…
- Obesity increases the risk of diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart disease and stroke.
- Arthritis of the knees and hips are more common in people who are overweight, and back pain is increased as well.
- Sleep apnea (which is a sleep disorder where there is blockage of airflow to the lungs intermittently during sleep) is common in people who are obese and is related to excessive fat deposits in the neck.
- In women, obesity can be associated with irregular menstruation and infertility, and in men, it is associated with reduced testosterone levels.
- Other complications include fatty liver disease, various cancers, breathing problems
How to lose weight?
The equation for weight loss relies on the balance between energy (or calories) coming into the body, and energy out (energy expenditure).
Energy in = amount of calories consumed from food
Energy out = energy expenditure, which is mostly our metabolism (energy used by our body to perform basic functions such as breathing, eating, circulating blood), and exercise
Energy in > energy out = weight gain
Energy in < energy out = weight loss
So, to lose weight, we either have to reduce energy in (by consuming fewer calories) or increasing energy out (by exercising more).
On average, a person burns around 60-65 calories by running 1km, and a nasi lemak with fried chicken is around 650calories (which is equivalent to running 10kms). As we can see, reducing 'energy in' is a much easier way to lose weight compared to increasing 'energy out'.
How to reduce energy in?
Dietary restriction is key. There are a few factors to consider:
- Portion control (reduce the amount of food taken)
- Type of food: fat has a lot more calories than carbohydrate and proteins. Therefore, by reducing fatty food such as fatty meat, food containing cream and butter and various processed food, one may be able to reduce the total caloric intake.
- Fasting or time-restricted eating:
a) Intermittent fasting is an increasingly popular way of losing weight. The typical regime is 16:8, meaning 16 hours of fasting (eg from 8 pm to 12 pm, skipping breakfast), and 8 hours of feeding (eg from 12 pm to 8 pm). During the fasting period, you are not allowed any calorie-containing food or snacks, but water, black coffee, black tea or green tea without milk and sugar is allowed.
b) By fasting, you will be skipping 1 meal a day, and therefore reduce the amount of calorie intake. This also forces you to avoid snacking, which is often a source of excess calorie intake. Intermittent fasting is also associated with other benefits such as improving insulin sensitivity, reducing inflammation and may prolong life expectancy.
c) However, not everybody is suitable for intermittent fasting, and people with underlying health conditions should consult your doctor prior to starting intermittent fasting.
- Another method of weight loss is by use of meal replacements. Sometimes, this is called VLCD, or very low-calorie diet. This involves replacing main meals such as lunch or dinner with a liquid type diet (commercial VLCD products are available, such as Optifast) that contains only around 250 calories. A typical meal contains around 500-700 calories, and by using meal replacements, calories consumed per meal is much reduced.
Are there other methods of weight loss?
- There are medications that may assist with weight loss. However, these medications may not be suitable for everyone and may be associated with side effects. Medications are usually only considered for individuals with a BMI of >30, or for those who are overweight and have complications related to obesity, such as diabetes, hypertension and et cetera.
- Surgery is a highly effective means of weight loss, and for those who are severely overweight, this should be considered as surgery typically leads to a sustained long term reduction in weight, with significant reductions in complications related to obesity.
- Do talk to your doctor for more information on medications for weight loss or weight loss surgery (also known as bariatric surgery).






Leave a Reply